Streaming in Healthcare: The Medical Industry’s Swiss Army Knife (Update)

From the rapid adoption of telehealth during the COVID-19 health crisis to the 20 million endoscopies performed annually in the United States, healthcare innovators are using streaming to improve medical outcomes and push the industry forward.
The benefits of this are far-reaching. For one, streaming can bring the expertise of remote doctors to every corner of the world. Just imagine relying on a leading London-based neonatologist to treat a baby born four months premature in rural India.
Beyond that, streaming technology delivers 360-degree insight into internal ailments. Medical professionals use video-enabled devices to remove polyps, examine the causes of chronic irritation, perform robotic surgeries, and make successful diagnoses.
Live streaming has even found its way into education and awareness. Two doctors teamed up to live stream a colonoscopy back in 2016 with the goal of demystifying the procedure. They leveraged video as a form of outreach to show reluctant patients how undergoing regular exams can easily prevent the second-leading cause of cancer-related death in the U.S.
Recently, video-enabled telehealth has also proven instrumental in containing the spread of infectious diseases. Virtual doctor visits, remote patient monitoring, and the use of healthcare robots have surged in 2020 — all of which reduce the need for people to physically interact with one another in hospital settings.
Below, we explore the myriad ways that streaming technology is revolutionizing healthcare.
Streaming in Education
Knowledge transfer comes easy with the help of live streaming. Accessibility and affordability have both been the driving forces behind using streaming for medical education. The technology can be used for classroom instruction, simulations, and even remote consultations. And because streaming supports live video delivery across the world, it ensures that our global healthcare community stays woke on the most cutting-edge training and procedures.
During the coronavirus crisis, though, live surgical broadcasts have become one of the few ways to bring students and additional experts inside of operating rooms. And while the pandemic has catalyzed this change, we expect adoption to continue due to the convenience and efficiencies streaming delivers.
Camera-Aided Surgery
Hospitals rely on integrated streaming technology to improve surgical outcomes and enhance patient care. From laparoscopies and endoscopies to any robotic surgery, streaming allows doctors to perform minimally invasive operations that reduce recovery time for patients. Doctors can leverage 3D high-definition cameras to perform surgeries easily and quickly. Plus, by controlling robotic arms, surgeons benefit from a clearer view of the operation and less fatigue.
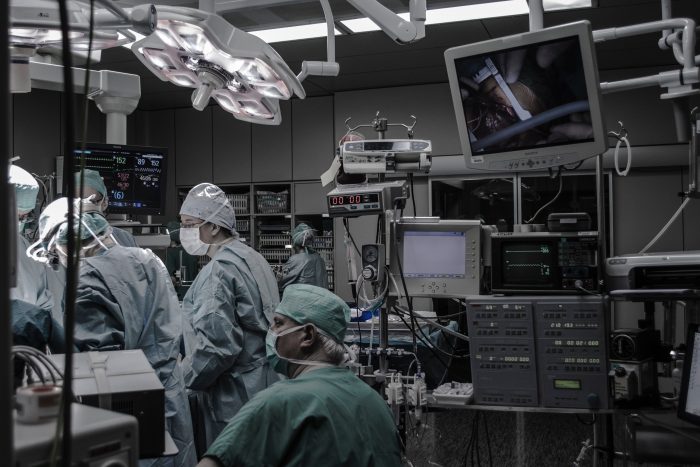
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) and Video-Enabled Devices
Camera-aided surgery has long played a role in hospital settings, but what about the use of nonsurgical robotics in healthcare facilities? Meal deliveries, disinfection routines, and specimen transportation are all being delegated to these intelligent machines as hospitals look to reduce exposure.
Likewise, internet-connected medical devices are on the rise. An estimated 20-30 billion Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices are in use today and the number continues to grow. Many of these take the form of wearable health technology, which enables the sharing of real-time health metrics such as blood pressure, temperature, heart rate, and more.
Google Glass, for instance, embeds streaming technology into a pair of glasses. Wearers can consult remote experts across the globe — while continuing on with their work. The voice-controlled device uses augmented reality (AR) to display additional data in the periphery of sight and integrates with existing Google applications. This type of device has already found traction in healthcare, enabling surgeons to view patients’ vital statistics during procedures. The hands-free technology also prevents the spread of germs, something we’ve all become hyper-aware of in 2020. 5G will extend these capabilities beyond operating rooms to include mobile users with wearable devices designed for the healthcare industry.
Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics
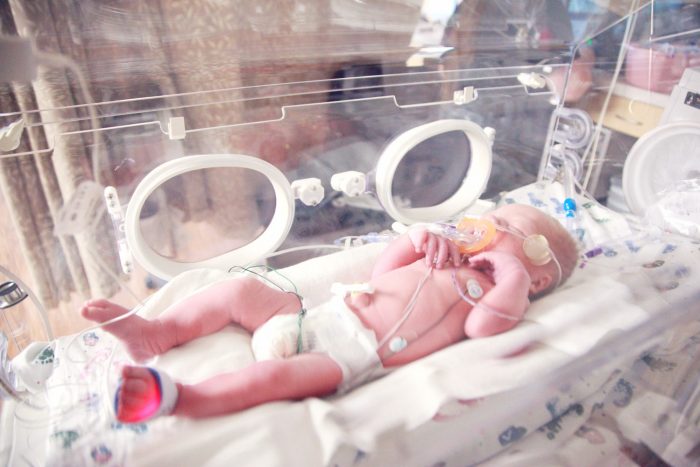
Innovation means using video in ways that it’s never been used before. Many organizations have capitalized on streaming technology to extend medical expertise to rural areas. As one heartstring-pulling example, Child Health Imprints built streaming into an internet of things (IoT)-enabled device for neonates.
The cloud-hosted appliance assimilates real-time data from the disparate biomedical devices used to monitor preterm infants — including ventilators, monitors, and blood gas analyzers. In addition to reducing time-to-treatment and improving quality of care, the product enables remote monitoring of neonates in rural regions via video streaming.
Streaming also powers virtual doctor visits, wherein a patient can video conference with a doctor rather than physically traveling to an office. Emergency 911 centers are even deploying real-time video capabilities to dispatchers to enhance medical triage.
For example, the public safety technology company Carbyne connects emergency call centers with video call functionality. Each time someone in need makes an emergency call to a center leveraging Carbyne’s platform, they are prompted to enable a live video stream. This provides additional information to call-takers and paramedics about the patient’s physical wellbeing and location. In the video below, we take a closer look.
Clinical Communications
Healthcare facilities are overcoming the obstacles of social distancing by deploying around-the-clock live video tools to communicate with family members outside of the hospital. One clinical communication platform, AngelEye Health, allows families to keep an eye on their newborn baby while being cared for in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
The solution has always provided parents reassurance by connecting them with a 24/7 feed and updates on their baby’s status. But with recent restrictions to hospital visitations, the platform has helped assuage the disruptions of COVID-19. When mothers and fathers can’t physically be with their newborn child, AngelEye Health delivers the next best alternative.
Requirements of Streaming in Healthcare
So, what exactly is required to make live streaming in healthcare successful? Quality and low latency, for starters. Successfully performing a coronary bypass would be near-impossible with a grainy display or significant lag. Reliability and security are also must-haves. In the age of HIPAA, video-assisted surgery wouldn’t be permitted without bulletproof protection of such data. Finally, when it comes to education and training, global scalability plays a significant role.
For whatever you’re trying to achieve, Wowza’s full-service streaming platform provides reliable, low-latency video capabilities that can be embedded into any product or service. That’s why Karl Storz, the leading endoscope manufacturer, leverages Wowza to power their medical products. Our technology is also built into Stryker Corporations’ portfolio of medical products, Child Health Imprints’ IoMT devices, and Carbyne’s emergency 911 platform.
Conclusion
Live streaming is democratizing medicine. Doctors-in-training around the world can access educational streams of experts in their field, and people in need of medical attention are no longer limited to the practitioners in their neck of the woods. Telehealth promised to make the industry more cost-effective — not to mention convenient. And 5G will extend these capabilities beyond just the home, to include mobile users without a Wi-Fi connection.




