Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): What It Is and the Future of Connected Health
We’ve long relied on ‘things’ to assess and treat our health. Things like thermometers, pills, x-ray machines, and even artificial knees. But increasingly, these things are becoming smart, connected, and in communication with each other.
Sound like science fiction? Well, if you’ve ever worn a Fitbit, then you’re an early adopter.
The internet of medical things (IoMT), also known as healthcare IoT, describes almost any type of internet-connected medical or wellness device. From smart stethoscopes to consumer wearables, examples of this trending development in healthcare tech continue to pop up.

An estimated 20-30 billion IoMT devices are in use today.1
What Is IoT?
Let’s start with the internet of things (IoT). Oxford Languages defines IoT as “the interconnection via the internet of computing devices embedded in everyday objects, enabling them to send and receive data.”
Well-known applications of IoT include smart doorbell cameras and Amazon’s long-awaited delivery drones. Basically, any ‘thing’ that uses the internet to enhance its ability to complete tasks is likely a part of IoT. Unlike regular computers, these objects are designed to communicate and act autonomously, without requiring human intervention.
They also often serve a primary function outside of computing. For instance, a Roomba is first and foremost a vacuum. But the addition of its backend IoT infrastructure makes it so much more than that.
These things — as well as the people, computers, and data they interact with — combine to create smart ecosystems.
What exactly do I mean by that? Well, going back to the Roomba, the S9+ model uses camera-based navigation to learn the layout of your home. It also integrates with Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant to respond to voice commands and empties itself once full. In this way, it becomes one dynamic component of a smart house made up of connected assistants, vacuums, refrigerators, thermostats, and lights.
Another example of a smart ecosystem would be smart hospitals — which brings us to the internet of medical things (IoMT).
What Is IoMT?
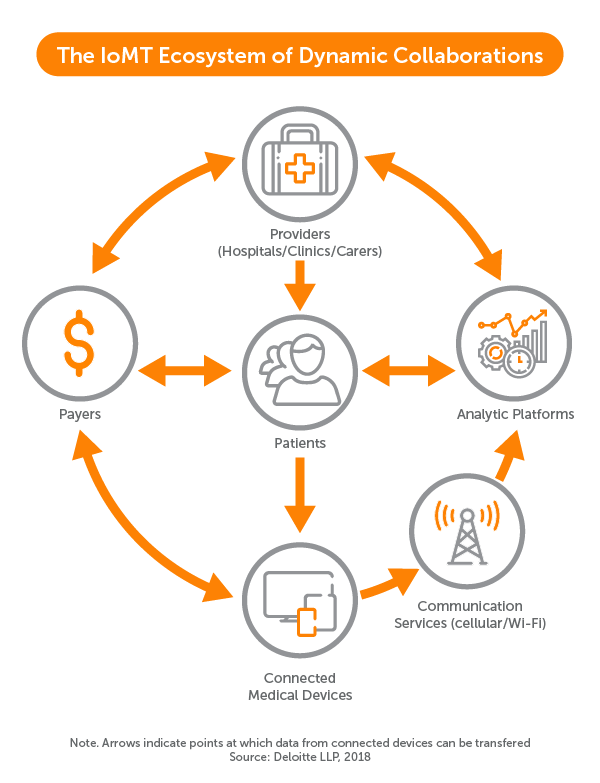
IoMT and healthcare IoT are two ways of describing the connected infrastructure of medical devices that doctors, patients, and consumers now rely on. Surgical robots and intelligent monitoring equipment within hospitals are certainly great examples of IoMT, but so too are the everyday fitness trackers and smart sock baby monitors that today’s shoppers flock to.
To quote Deloitte:
“The IoMT brings together people (patients, caregivers, and clinicians), data (patient or performance data), processes (care delivery and patient support), and enablers (connected medical devices and mobile applications) to deliver improved patient outcomes efficiently.”
Healthcare networks are complex. So, any opportunity to improve collaboration and automation across these ecosystems is a no-brainer. Healthcare IoT achieves just that. That’s why intelligent hospital beds can now communicate with nurse’s stations each time a patient falls. Likewise, a digital kiosk might delegate tasks to specimen transportation robots and sanitation robots depending on the patient’s needs.
IoMT also enables on-the-go healthcare by transforming the physical hospital into something virtual. Rather than forcing patients to stay in a facility for observation, wearable devices support remote patient monitoring. IoMT technologies also show promise in long-term care by making it possible for senior citizens and other vulnerable populations to stay in their own homes longer.
And so, when we talk about connected healthcare ecosystems, we might be referring to smart hospitals powered by camera-aided surgical devices, digital kiosks, and nonsurgical robotics. But increasingly, these connected ecosystems extend well beyond the clinic walls.
The Role of Wearable Technology in IoMT

The global wearable devices market is expected to reach $62.82 billion by 2025.2
Medical technology is infusing every step of the healthcare journey with connected solutions for real-time monitoring and analysis.
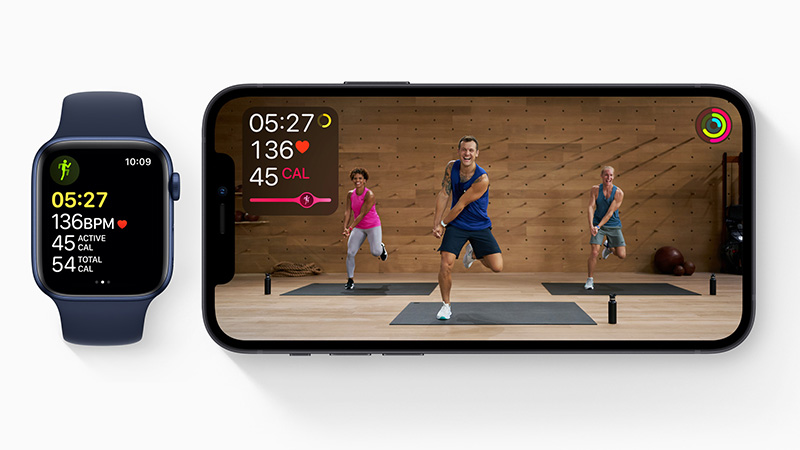
Take the Apple Watch Series 6 as exhibit one. The smart wristband allows wearers to read their blood oxygen levels, track their sleep, take an ECG, and detect if they’ve washed their hands. Alerts go off when heart rate dips too low or spikes too high. Plus, the device comes with a subscription to Apple Fitness Plus, Apple’s digital fitness offering designed to compete with Peloton.
Health and fitness are now the Apple Watch’s two biggest selling points. As such, Apple’s coined a new tagline for the apparatus: “The future of health is on your wrist.”
It should come as no surprise that Apple has made their intentions within healthcare IoT clear. In an interview with Outside magazine, CEO Tim Cook revealed: “I really believe that if you zoom out to the future and then look back and ask, ‘What has Apple’s greatest contribution been?’ it will be in the health and wellness area.”
If Apple (a.k.a. the world’s most valuable company) is eyeing an industry, one thing is sure: Innovation will follow. But what exactly does it take to compete in this arena?
The Technology Behind IoMT
Three factors make IoT possible:
- High-speed wireless technologies like 5G
- Advances in computing power and data compression
- The subsequent miniaturization and portability of electronic devices
What plumbing infrastructure does for fluids, healthcare IoT achieves for health data. We can’t see it, but a network of connected apparatuses keeps everything moving seamlessly. And dynamic processes occur at multiple intersections.
IoT applications do this by leveraging sensors to collect data and analytics platforms to make sense of it all. For many IoMT devices — including endoscopic instruments, smart baby monitors, and telehealth kiosks — video streaming is also a critical capability.
Streaming-enabled IoT can deliver 360-degree insight into internal ailments, bring the expertise of remote doctors to every corner of the world, and contain the spread of infectious diseases by reducing the need for people to physically interact in hospital settings.
All that said, it’s impossible to discuss the technology enabling IoT applications without also mentioning the most significant vulnerability in digital healthcare environments: content security. Complying with regulatory bodies like HIPPA and the FDA requires content protection at every layer — including encryption, two-factor authentication, and the like.
Healthcare IoT Products
To get a feel for just how limitless the IoMT space is, here’s our list of the connected gadgets currently out there in 2021.
- Robotic surgical instruments: Most commonly used for laparoscopies and endoscopies, streaming-enabled robots allow doctors to perform minimally invasive operations that reduce recovery time for patients.
- Nonsurgical robots: Meal deliveries, disinfection routines, and specimen transportation are all being delegated to intelligent machines as hospitals prioritize reducing exposure.
- Remote monitoring: Chronic disease management solutions and sophisticated telehealth systems for rural populations can leverage remote patient monitoring devices to transmit health data like blood pressure, oxygen, blood sugar, etc.
- Medical alert systems and emergency response: Next-generation 911 technologies and personal emergency response systems (PERS) now integrate video streaming, dynamic location detection, and other functionalities to ensure that all information is gathered without wasting time.
- Medication adherence solutions: Smart pills that transmit data to indicate that they’ve been swallowed might sound a bit extreme, but even intelligent packaging could improve health outcomes. Studies show that when patients are aware that their treatment habits are being tracked, their adherence improves by almost 20 percent.
- Data automation: IoMT devices can help speed up decision-making by collecting, reporting, and analyzing bulky data in real-time.
- Clinical-grade wearables: Examples of clinical-grade wearables include headsets used to treat depression, belts to provide protection in case of falls, and wearable pain relief.
- Personal wellness wearables: From smart garments to fitness tracking wristbands, personal wellness wearables are becoming more advanced by the day.
- Telehealth: Seeing a doctor no longer requires physical interactions thanks to healthcare IoT. Kiosks for remote treatment via video streaming now combine the best aspects of telehealth with those of in-office visits by facilitating the ability to assess temperature, blood pressure, and other biometrics.
- Logistics: Whether safely transporting and storing COVID-19 vaccines or future-proofing the medical supply chain for the next pandemic, IoMT ecosystems with streaming-enabled drones and autonomous trucks are sure to play a role.
Benefits of Healthcare IoT
Healthcare companies of the future will be technology companies. And IoMT is the connective tissue of next-generation healthcare. It informs innovative, personalized medical strategies and makes the treatment process seamless from primary care through specialists. These connected ecosystems will also enable the industry to move from a reactive and ad-hoc model of care to one that is predictive, preventative, and holistic.
The benefits are endless. But to name a few, IoMT:
- Improves patient outcomes by boosting accessibility
- Empowers patients to take control of their health
- Drives efficiencies and streamlines communication
- Prevents the spread of disease with solutions for in-home care
- Allows for convenience and brings expertise to remote areas
- Enhances collaboration across healthcare teams
- Provides a more holistic view to providers
The Role of Video Streaming
Video streaming is among the more prevalent capabilities making healthcare IoT possible. And for that, you can rely on Wowza. Built to build on, our technology can sit in any environment — whether it be an IoT device for remote patient monitoring or a cloud-based emergency call management platform.